Designing of a Dexterous Hand and Performance Evaluation Based on Teleoperation November 2024
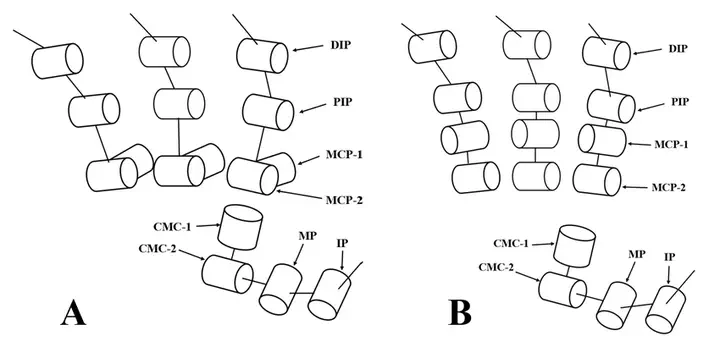 A-Joint-distribution-diagram-of-C-Hand-10-B-Joint-distribution-diagram-of-Leap-Hand
A-Joint-distribution-diagram-of-C-Hand-10-B-Joint-distribution-diagram-of-Leap-HandAbstract
We proposed to design and evaluate a dexterous robotic hand through teleoperation. We introduced a dexterous hand with four fully actuated fingers, providing 16 degrees of freedom. A motor independently controls each joint, ensuring precise and flexible movements. The design incorporates an innovative joint distribution structure, enhancing the hand’s flexibility and grasping capabilities. To validate the effectiveness of the design, we conducted a series of real-world experiments where the robotic hand replicated natural finger movements based on human hand gestures. The results demonstrated that the hand pose retargeting method successfully translates human gestures into precise and functional robotic hand movements, highlighting its potential for various practical applications in robotics.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.